
Example
| TAS: | 110kts | Variation: | 12°E |
| Wind: | 320/10 (true) | Distance: | 100nm |
| TRK: | 350° (true) |
Before we start, we need to convert all bearings from true to magnetic.
When variation is East, subtract from true bearing. When variation is West, add to the true bearing.
| Wind: | Wind ± Variation = 320° – 12° = 308/10 |
| TRK: | TRK ± Variation = 350° – 12° = 338° |
To find the Crosswind and Headwind components, Heading required, Ground speed and Time, follow thse steps.

-
On the wind side of your CR2 computer, Point the TAS
 marker on the middle circle, to the IAS on the outer marker.
marker on the middle circle, to the IAS on the outer marker.

-
On the inner circle, place the wind speed against the
TC marker, and using a pencil, mark down the wind speed
marker, and using a pencil, mark down the wind speed

-
Turn the inner circle until the TRK meets the
 marker
marker
-
Find the Crosswind and Headwind components
XW: ~5kts HW: ~7kts
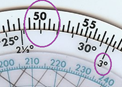
-
Locate the XW value on the outer circle, then look at the middle circle to find the nearest whole degree. This represents the amount of drift.
Drift: 3° -
For a left crosswind, add the drift to the TRK to determine Heading (HDG)
For a right crosswind, subtract the drift from the TRK to determine HDG.HDG: TRK ± Drift = 338° + 3° = 341° -
To find ground speed, subtract the headwind, or add the tailwind component to the IAS
GS: IAS ± HW = 110kts – 7kts = 103kts -
To find time required to travel a distance, use this formula:
Time = Distance ÷ Ground Speed
